Commands
Get unique values
SELECT DISTINCT report_date FROM daily;
How many records?
SELECT count(*) from vanall WHERE Shipped_Date="2021-01-12";
Last Shipped Date
-- Current max date in the table
SELECT max(Shipped_Date) from vanall;
Insert Or Update
INSERT or replace INTO daily (date,name_id,testing_hour,sellable,liquidation,quality,concession)
VALUES ("2021-02-01",5,1.0,2,3,4,5);
Insert data get from other tables
-- insert new data from temp into table vanall
INSERT INTO vanall
SELECT * from temp where Shipped_Date>"2021-01-12";
Update
UPDATE associate SET show=1 WHERE show IS NULL
Delete
-- remove all the assets that are not shipped yet
DELETE FROM vanall WHERE Shipped_Date is NULL
-- delete table
DROP TABLE associate;
Creating Sub-Query
with yvr3(facility,class,cat, sub) as
(select "YVR3", class,cat, count(*) as sub from amazon where location < "QC-76.11"
group by class,cat),
yyc1(facility, class,cat,sub) as
(select "YYC1", class,cat,count(*) as sub from amazon where location > "QC-76.10"
group by class,cat)
select yyc1.facility,yyc1.class,yyc1.cat, yyc1.sub from yyc1
left join yvr3
on (yyc1.class=yvr3.class and yyc1.cat=yvr3.cat)
where yvr3.cat is null
order by yyc1.sub desc;
FULL OUT JOIN
Sqlite doesn’t support FULL OUT JOIN or RIGHT JOIN.
It’s easy to perform a RIGHT OUTER JOIN in SQLite by simply reversing the order of tables and using a LEFT OUTER JOIN.
It’s also possible to do a FULL OUTER JOIN by combining LEFT OUTER JOINs using the UNION keyword.
See Full Out Join Example on how to emulate full out join in Sqlite.
How to convert datetime to string?
See Data and Time functions in Sqlite
SELECT strftime("%Y-%m-%d",datetime('now','localtime'))
-- output: 2021-07-07
SELECT strftime("%s",datetime('now'))
-- output: 1625763745
Create Table
create table associate (
first TEXT NOT NULL,
last TEXT NOT NULL,
-- Generated column: only AS keyword and the parenthesized expression is required
full TEXT AS (last ||', '|| first) STORED,
-- Current timestamp as default value: 2021-07-09 19:09:06 (UTC/GMT timezone)
created TEXT NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
-- local timestamp: not recommanded
modified TEXT NOT NULL DEFAULT (datetime('now','localtime'))
);
How to create a table from a template table?
CREATE TABLE new_table
AS
SELECT *
FROM existing_table
WHERE 1 = 0;
Note that this approach might not replicate constraints like primary keys, foreign keys, or indexes. If you want to copy the entire schema including constraints,
you’ll need to use a more manual approach by running a CREATE TABLE statement
with the same column definitions and constraints explicitly.
Default value
If the default value of a column is CURRENT_TIME, CURRENT_DATE or CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, then the value used in the new row is a text representation of the current UTC date and/or time.
- For CURRENT_TIME, the format of the value is “HH:MM:SS”.
- For CURRENT_DATE, the format of the value is “YYYY-MM-DD”.
- For CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, the format of the value is “YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS”.
Note: When having a column defined with “NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP”, inserted records will always get set with UTC/GMT time.
-- show the timestamp as local time zone
SELECT datetime(created,'localtime'), created from associate;
-- output: 2021-07-09 14:57:00 2021-07-09 21:57:00
Generated Columns or Computed Columns
Generated columns (also sometimes called “computed columns”) are columns of a table whose values are a function of other columns in the same row. Generated columns can be read, but their values can not be directly written.
Generated columns can be either VIRTUAL(default if missing) or STORED.
The value of a VIRTUAL column is computed when read, whereas the value of a STORED column is computed when the row is written.
CREATE TABLE t1(
a INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
b INT,
c TEXT,
d INT GENERATED ALWAYS AS (a*abs(b)) VIRTUAL,
e TEXT GENERATED ALWAYS AS (substr(c,b,b+1)) STORED
);
Sqlite: Get table information
PRAGMA table_info(mytable)
Expressions
Concat
The || operator is “concatenate” - it joins together the two strings of its operands.
SELECT last || ", " || first FROM associate;
Like and Escape
%: zero or more characters_: one character
-- Labels end with 30126
SELECT Label from RL WHERE Label LIKE '%30126';
-- Contains 10%
SELECT Label from RL WHERE Label LIKE '%10\%%' ESCAPE '\';
Datetime
-- select data between two dates
SELECT * FROM User WHERE date_of_birth BETWEEN date(:from) AND date(:to)
-- compare date
select * from user where date_of_birth=Date(:date)
-- group by Year
SELECT strftime('%Y', date_of_birth) as year,count(date_of_birth) as count FROM User GROUP BY date_of_birth
-- Select data for a specific year
SELECT * FROM User WHERE strftime('%Y', date_of_birth) = :year
-- get Last month Data
select * from User where created_date>=datetime('now', 'now', '-30 day')
-- Order by Date
select * from User ORDER BY date(date_of_birth) asc
-- calculate age from birth date
SELECT *, cast(strftime('%Y.%m%d', 'now') - strftime('%Y.%m%d', date_of_birth) as int) as age FROM User
FAQ
What’s the difference between UNION and JOIN?
Both Joins and Unions can be used to combine data from two or more tables. In short, JOIN combine columns, UNION combine rows
JOIN
- It combines data from many tables based on a matched condition between them
- It combines data into new columns
UNION
- It combines the result-set of two or more
SELECTstatements - It combines data into new rows
- Number of columns selected from each table should be the same
UNION(slower) removes the duplicate rows while the UNION ALL(faster) includes the duplicate rows in the final result set.
SELECT dScanIDShippedDate, vLabel, vSerialNumber FROM Vancouver WHERE dScanIDShippedDate > '2020-10-01'
UNION ALL
SELECT dScanIDShippedDate, vLabel, vSerialNumber FROM Toronto WHERE dScanIDShippedDate > '2020-10-01';
Work
How to get Liquidation Class & Category Report
- Download the latest Inventory All Fields file from Egnyte
- Import the CSV data into a temp database(
RL). See CSV - Execute the following command to get the report data.
SELECT Asset_Tag, Class, Category, Mfg, Model_Number,
Repair_Disposition, Final_Functional_Status,
Audit_Final_Notes, Total_Fees, BER_Threshold_Percentage,
BER_Threshold, BER_Threshold_Remaining
FROM RL
WHERE Shipped_Date >= "2021-03-07" AND Shipped_Date <= "2021-03-13" AND Last_FG_Site = "FG(RL-LIQ)"
- Copy all the data from DB Browser and Paste the data into “Weekly-Stats-Template.xlsx”
- Save it as
20210316 - RL Liquidation Report.xlsx - Remove the two yellow columns and save it as
20210316 - Amazon Liquidation Report.xlsx - Attach these two files and send the report
How to get the associates’ daily/weekly testing details report?
To Get the Sellable(including Fraud) and Liquidation assets details for each associate.
WITH a AS(
SELECT Auditor, count(*) AS sellable
FROM RL
WHERE Date_put_to_FG_Site >= "2021-03-07" AND Date_put_to_FG_Site <= "2021-03-13" AND (Repair_Disposition = "COMP" OR Repair_Disposition = "FRAUD")
GROUP BY Auditor),
b AS (
SELECT Auditor, count(*) AS liq
FROM RL
WHERE Date_put_to_FG_Site >= "2021-03-07" AND Date_put_to_FG_Site <= "2021-03-13" AND (Repair_Disposition = "LIQC" OR Repair_Disposition = "LIQF")
GROUP BY Auditor)
SELECT a.Auditor AS auditor, a.sellable, b.liq FROM a
LEFT JOIN b ON a.Auditor = b.Auditor
UNION ALL
SELECT b.Auditor AS auditor, a.sellable, b.liq FROM b
LEFT JOIN a ON a.Auditor = b.Auditor
WHERE a.Auditor IS NULL
ORDER BY auditor
Import
Import CSV file Into Sqlite Database
We have inventory all fields file which is in CSV format. There’re several methods to load these data into database for further processing.
Import CSV file from command line
Download and install SQLite. From command line execute the following commands to import your CSV file into a table:
Note: All the columns’ data types are TEXT
C:\Sqlite> sqlite
sqlite>
sqlite> .mode csv
sqlite> .import rl.csv assets
sqlite> .schema assets
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS "assets"(
"Facility" TEXT,
"Source" TEXT,
"Source_Location" TEXT,
...
);
sqlite> .save assets.db
sqlite> .quit
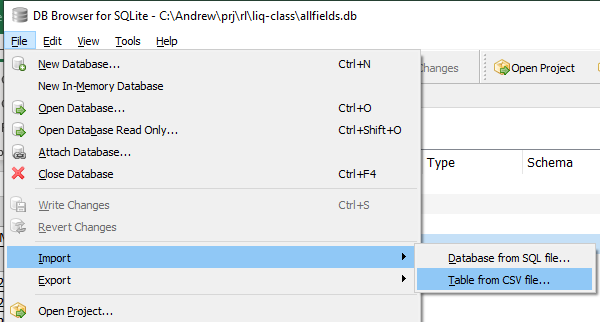
Import data by using DB Browser
DB Browser for SQLite (DB4S) is a high quality, visual, open source tool to create, design, and edit database files compatible with SQLite.
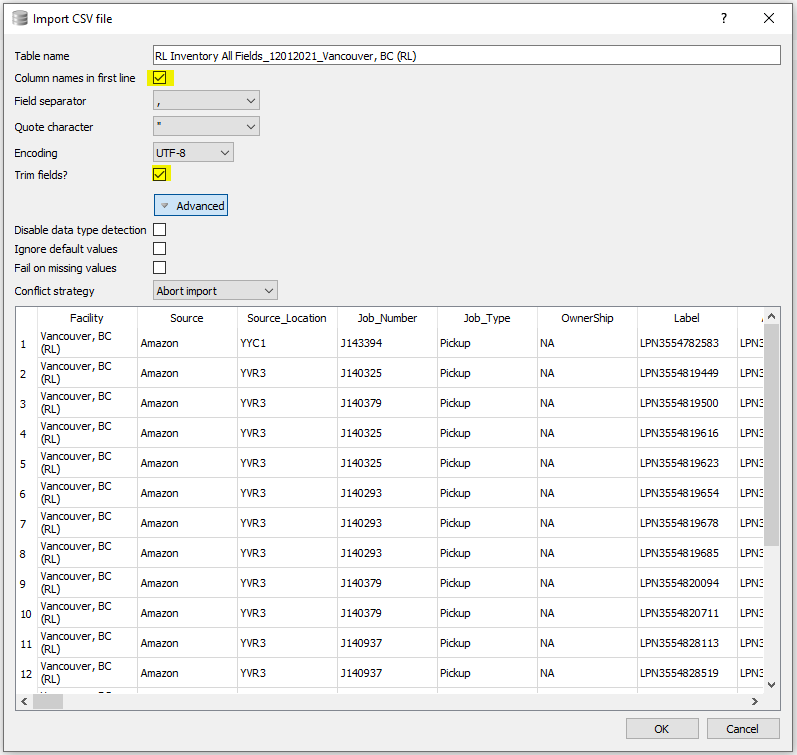
To import CSV data using DB4S, select File > Import > Table From CSV File...
Import Options:
- Table name: assets
- Column names in first line: Yes, the first line can be used as column names
- Disable data type detection: Leave it unchecked so that DB4S can detect the column types
- Click OK to import it
DB4S can detect the column data types: TEXT, INTEGER, REAL, etc.
Tips:
- You can use
PRAGMA table_info(table_name)to get all the column names of a table. - You can get the table create statement from Database Structure tab